貨號
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN41901R-50ul
50ul
¥1486.00
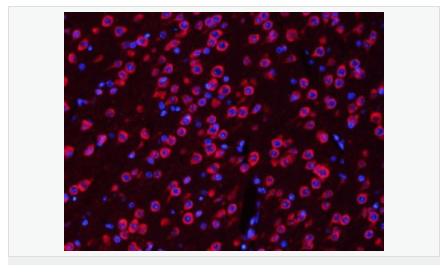
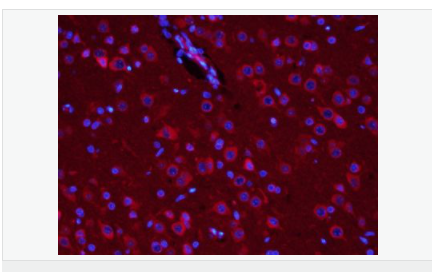
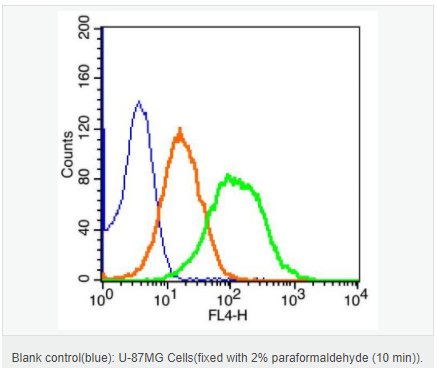
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41901R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
BN41901R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Rabbit) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,Flow-Cyt,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
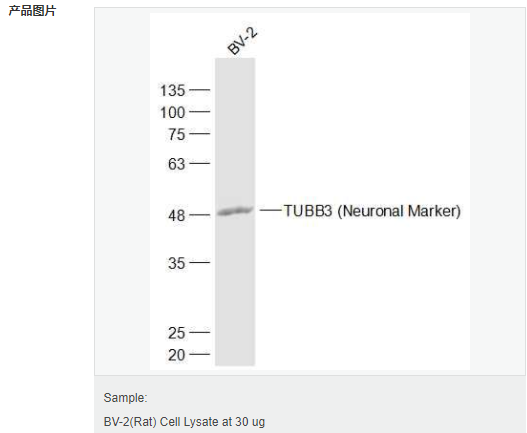
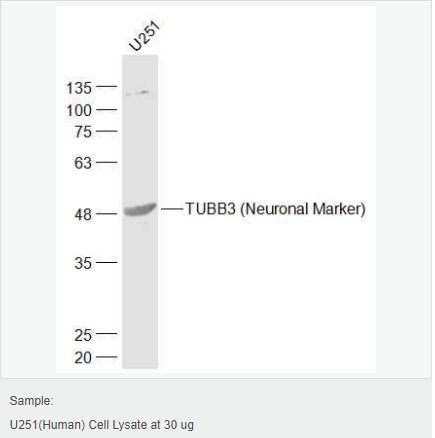
| 英文名稱 | TUBB3 (Neuronal Marker) |
| 中文名稱 | 神經(jīng)細(xì)胞特異性微管蛋白抗體 |
| 別 名 | Neuron specific beta III Tubulin; beta 4; MC1R; TBB3_HUMAN; TUBB 3; TUBB 4; TUBB3; TUBB4; Tubulin beta 3 chain; Tubulin beta 4; Tubulin beta III; Tubulin beta-3 chain; Tubulin beta-4 chain; Tubulin beta-III; Beta tubulin III; Neuron specific beta III Tubulin. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 細(xì)胞生物 免疫學(xué) 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) 轉(zhuǎn)錄調(diào)節(jié)因子 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, Mouse, Rat, (predicted: Dog, Rabbit, ) |
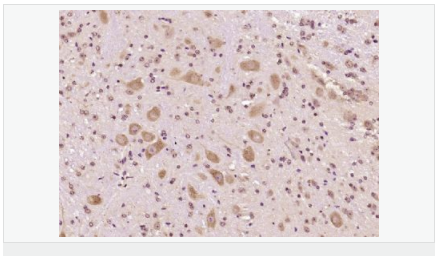
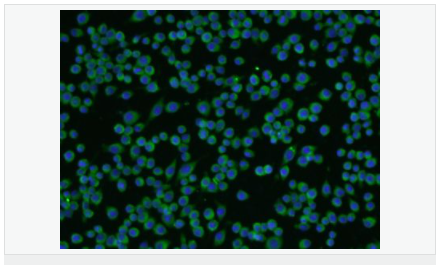
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 Flow-Cyt=1μg/Test ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:200-800 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 50-55kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞漿 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Neuron specific beta III Tubulin:401-450/450 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲(chǔ) 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | Neuronal Marker Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha-chain. TUBB3 plays a critical role in proper axon guidance and mantainance. Function: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha-chain. TUBB3 plays a critical role in proper axon guidance and mantainance. Subcellular Location: Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Tissue Specificity: Expression is primarily restricted to central and peripheral nervous system. Post-translational modifications: Some glutamate residues at the C-terminus are polyglutamylated. This modification occurs exclusively on glutamate residues and results in polyglutamate chains on the gamma-carboxyl group. Also monoglycylated but not polyglycylated due to the absence of functional TTLL10 in human. Monoglycylation is mainly limited to tubulin incorporated into axonemes (cilia and flagella) whereas glutamylation is prevalent in neuronal cells, centrioles, axonemes, and the mitotic spindle. Both modifications can coexist on the same protein on adjacent residues, and lowering glycylation levels increases polyglutamylation, and reciprocally. The precise function of such modifications is still unclear but they regulate the assembly and dynamics of axonemal microtubules. DISEASE: Defects in TUBB3 are the cause of congenital fibrosis of extraocular muscles type 3A (CFEOM3A) [MIM:600638]. A congenital ocular motility disorder marked by restrictive ophthalmoplegia affecting extraocular muscles innervated by the oculomotor and/or trochlear nerves. It is clinically characterized by anchoring of the eyes in downward gaze, ptosis, and backward tilt of the head. Congenital fibrosis of extraocular muscles type 3 presents as a non-progressive, autosomal dominant disorder with variable expression. Patients may be bilaterally or unilaterally affected, and their oculo-motility defects range from complete ophthalmoplegia (with the eyes fixed in a hypo- and exotropic position), to mild asymptomatic restrictions of ocular movement. Ptosis, refractive error, amblyopia, and compensatory head positions are associated with the more severe forms of the disorder. In some cases the ocular phenotype is accompanied by additional features including developmental delay, corpus callosum agenesis, basal ganglia dysmorphism, facial weakness, polyneuropathy. Similarity: Belongs to the tubulin family. SWISS: Q13509 Gene ID: 10381 Database links: Entrez Gene: 10381 Human Entrez Gene: 431043 Chicken Entrez Gene: 22152 Mouse Omim: 602661 Human SwissProt: Q13509 Human SwissProt: Q9ERD7 Mouse Unigene: 511743 Human Unigene: 40068 Mouse Unigene: 43958 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |